SPHERICAL BEARING
Spherical bearings, a bridge component at the interface of superstructure and substructure, consist of an assembly of spherical concave and convex plate playing an important role to give rotation mechanism and large translation of the structure. These bearings transfer large vertical loads and can accommodate relative movement of the structure as well.
Why spherical Bearings?:
1.This is a reliable High Load Multi-Rotation type bearing and It can be designed to accommodate large loads (100 MT to 10000 MT) and rotation of 0.04 rad. or even more under adoption of some special design.
2. Spherical Bearing have longer durability, enhanced service & performance life when compared with conventional Steel, Elastomeric & even Pot Bearings.
3. This can be used as Multi rotational Bearings.
4. Low height i.e more stable.
5. Negligible vertical deflection under load.
6. bearings allow three-dimensional movements, enabling large tilting angles with little resistance and less turning moments.
7. These bearings does not contain any elastomer or rubber which changes its property during service period due to extremities of temperature and elements of weather, hence more suitable over elastomeric bearing.
A labeled sketch of spherical bearing is shown in Fig-A below. Components of Spherical bearing are-
7. These bearings does not contain any elastomer or rubber which changes its property during service period due to extremities of temperature and elements of weather, hence more suitable over elastomeric bearing.
8. Suitable for low degree temperature even for as low as -50°C.
Working principle of spherical bearing:
9. Minimum sliding friction coefficient meaning thereby reduced reaction on the structure.
10. Large vertical loading capacity.
11. Allows for large horizontal displacement.
12. sliding friction coefficient is minimum.
13. High strengthened stainless steel makes it durable.
14. This bearing is considered most advanced and superior over other bearing in long span bridges even more than 60m span. They are used worldwide.
A labeled sketch of spherical bearing is shown in Fig-A below. Components of Spherical bearing are-
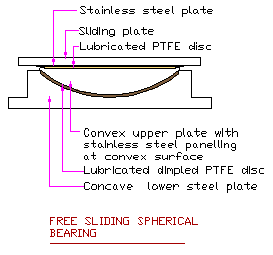
A. Sliding assembly consisting of
1. Steel Sliding
plate with attachment of stainless steel plate at the bottom which may also be of aluminium, brass or chrome.
2. Lubricated PTFE disc.
B. Rotation assembly consists of
3. Convex upper plate with
stainless steel panel at the convex surface.
4. lubricated dimpled PTFE disc between lower concave plate and upper convex plate. PTFE is popularly branded as Teflon
5. Concave lower steel plate.
 |
| Fig-A |
Lower spherical plate is firmly fixed with substructure concrete/pedestal. Top Sliding plate is firmly fixed to the bottom flange of superstructure girder through intermediate sole plate. There is a very low coefficient of friction at the interface of upper convex and lower concave plate due to smooth
stain less steel finishing and lubricated dimpled PTFE, in between two spherical plates.
Rotation Mechanism: Rotation is permitted by the rotation assembly. Position of upper convex plate changes by sliding over the lower concave plate due to its spherical shape permitting required rotation of bridge
girder with very low coefficient of
friction without any appreciable eccentric force. By the principle of ball-and-socket joint, rotation is permitted about all the three axes with minimum resistance. In addition, the spherical bearing surfaces due to low coefficient of friction enable large tilting angles with little resistance and less turning moments.
Translation: Translation is permitted by the sliding assembly at the top due to the movement of stainless steel plate attached to the steel slide plate over lubricated PTFE disc shown in the Fig-A. This bearing accommodates large translation in any direction on horizontal plane depending upon whether the bearing is guided or free sliding. Spherical bearing without sliding assembly does not permit translation rather rotation only.
Translation: Translation is permitted by the sliding assembly at the top due to the movement of stainless steel plate attached to the steel slide plate over lubricated PTFE disc shown in the Fig-A. This bearing accommodates large translation in any direction on horizontal plane depending upon whether the bearing is guided or free sliding. Spherical bearing without sliding assembly does not permit translation rather rotation only.
Types of spherical bearing:
a) Fixed spherical bearing- permits rotation only about all axes.
the top sliding plate all round slide guard is projected down to the lower concave plate to arrest translation in all direction Fig-B.
 |
| Fig-B |
the top sliding plate all round slide guard is projected down to the lower concave plate to arrest translation in all direction Fig-B.
b) Guided spherical bearing-permits rotation and translation in one direction only. In this bearing as in Fig-A above, slide guard is projected down from two parallel sides of the sliding top plate so that movement is allowed in the desired direction only i.e in long direction of the bridge in general.
c) Free sliding spherical bearing-
permits both rotation and translation in all direction i.e top sliding plate is free to move in all direction as shown in Fig-c.
 |
| Fig-C |
Forces/movement taken by the spherical bearing:
1. Vertical
loads is carried by all types of bearings.
2. Horizontal force in the transverse direction is resisted by the guided spherical bearing more efficiently i.e transverse movement is restricted in this bearing
3. Longitudinal movement is permitted by attachment of sliding assembly in all direction if the direction is not restricted.
4. Rotational displacement is permitted by all types.
With high strengthened steel body, spherical bearing is
especially designed for large vertical, horizontal and lateral loads and particularly where
large rotational structural displacements need to be accommodated.
Disadvantages:
1.
Require high degree of quality control and careful attention when installing.
2.
Requires periodic maintenance.
3. PTFE wears under service conditions and requires replacement after a period of service. Low temperatures, lack of lubrication, and contamination of the sliding interface with dust increasing the wear rate.
4. Corrosion of the stainless steel sliding plate.
5. These types of bearings are more expensive than pot bearings due to the machining required to give it the spherical shape and would only be used on major structures, to accommodate larger rotation.
6. The lateral load capacity is limited and wherever required , a separate system may be adopted to provide adequate resistance.
3. PTFE wears under service conditions and requires replacement after a period of service. Low temperatures, lack of lubrication, and contamination of the sliding interface with dust increasing the wear rate.
4. Corrosion of the stainless steel sliding plate.
5. These types of bearings are more expensive than pot bearings due to the machining required to give it the spherical shape and would only be used on major structures, to accommodate larger rotation.
6. The lateral load capacity is limited and wherever required , a separate system may be adopted to provide adequate resistance.







0 Comments